MUMBAI: RBI has forecast a growth of 6.7% for FY26 while cutting its growth estimate for FY25 to 6.4%, lower than the 6.6% projection made in its financial stability report released in Dec 2024. The central bank also predicts inflation to average 4.2% in FY26, staying within the target zone (2-6%).
In his maiden monetary policy statement RBI governor Sanjay Malhotra said improving employment conditions, tax relief in the Budget, moderating inflation, and healthy agricultural activity should support household consumption. However, govt consumption expenditure is expected to remain modest.
He added that higher capacity utilisation levels, robust business expectations, and govt policy support are favorable for fixed investment growth. Services exports are also expected to remain buoyant, supporting overall growth.
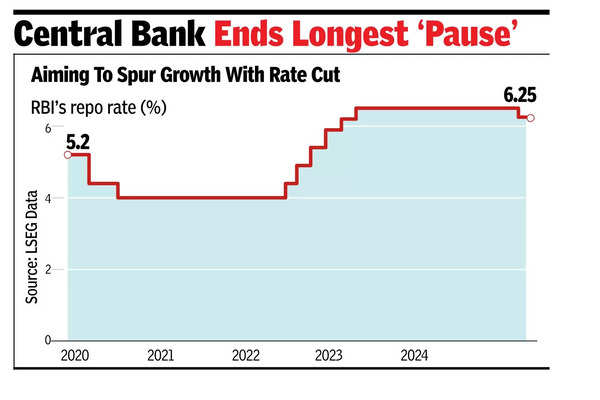
The monetary policy committee (MPC) on Friday decided to unanimously reduce the repo rate by 25 basis points (100bps = 1 percentage point) to 6.25% in line with market expectations.
Malhotra cautioned that global risks still loom. “Global headwinds, however, continue to impart uncertainty to the outlook and pose downward risks,” he said. Malhotra projected real GDP growth for the next year at 6.7%, with quarterly growth expected at 6.7% in Q1, 7.0% in Q2, and 6.5% in both Q3 and Q4.
The governor noted rising uncertainty in global financial markets, continuing volatility in energy prices, and adverse weather events as potential risks to inflation. “Rising uncertainty in global financial markets coupled with continuing volatility in energy prices and adverse weather events presents upside risks to the inflation trajectory,” Malhotra said.
CPI inflation for the current financial year is projected at 4.8%, with Q4 expected at 4.4%. Assuming a normal monsoon, inflation is expected to moderate to 4.2% in FY26. For the next financial year, CPI inflation is expected to be 4.5% in Q1, 4% in Q2, 3.8% in Q3, and 4.2% in Q4. Malhotra added that risks to inflation remain evenly balanced.


